Introduction to VoIP
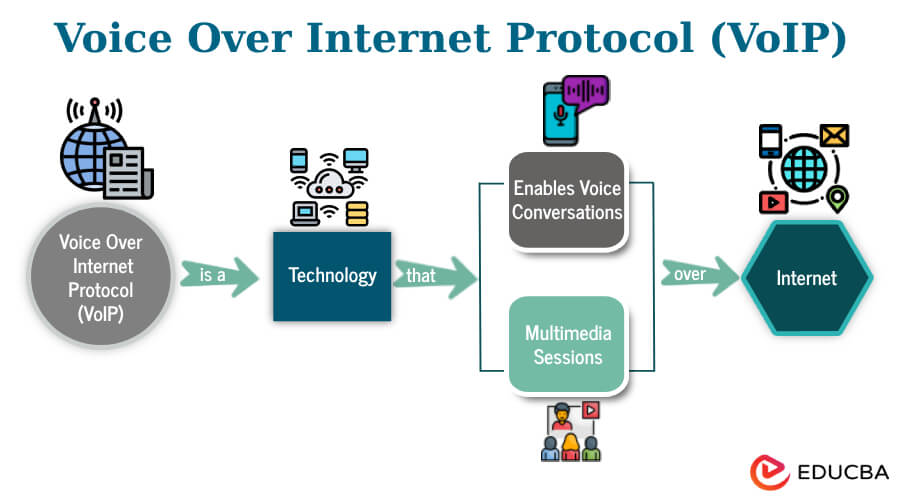
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), also known as Voice over IP, is a revolutionary technology enabling voice and multimedia communications over the Internet. Diverging from traditional telephone networks, VoIP utilizes IP-based networks to transmit voice data through digital signals. This distinctive approach offers a cost-effective and efficient means of communication by leveraging existing internet infrastructure.
VoIP converts analog audio signals into digital data packets, enabling seamless real-time communication. Devices such as computers, smartphones, and IP phones serve as conduits for this digital communication, breaking away from the constraints of traditional telephony.
Beyond its fundamental functionality, VoIP enhances communication experiences through various advanced features. These include call forwarding, video conferencing, and voicemail, elevating VoIP to a flexible and scalable solution. This technology caters to the needs of both individuals and businesses, providing an affordable and versatile platform for voice communication in the modern digital landscape.
Table of contents
History of VoIP
The history of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) traces back to the early days of computer networking and the development of the Internet. Here is a brief overview of the critical milestones in the history of VoIP:
- 1973-1974: Network Voice Protocol (NVP): The groundwork for VoIP began with the creation of the Network Voice Protocol during experiments conducted by the United States military’s ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network). This early attempt at transmitting voice-over data networks laid the foundation for future VoIP technologies.
- 1991: First Internet Phone Software: The first practical implementation of VoIP came in 1991 when VocalTec, an Israeli company, developed Internet Phone software. With the help of speakers and a microphone, users may place audio calls via the Internet with this program. Compared to traditional telephones, the quality was poor, and the user experience was simplistic.
- Late 1990s: H.323 Standardization: The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) introduced the H.323 protocol in the late 1990s, providing a set of standards for the transmission of audio, video, and data over IP networks. H.323 laid the groundwork for VoIP technology to become more standardized and interoperable.
- Early 2000s: Broadband Adoption: The widespread adoption of broadband internet connections significantly improved the quality and reliability of VoIP calls. Higher bandwidth facilitated smoother voice transmission and paved the way for the growth of consumer and business VoIP services.
- Mid-2000s: SIP Protocol Emergence: The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) gained prominence as an alternative to H.323. SIP simplifies initiating, modifying, and terminating interactive user sessions involving voice, video, messaging, and other communications applications and services.
- 2003: Skype Launch: Skype, a peer-to-peer VoIP service, was launched in 2003 and was crucial in popularizing internet-based voice communication. It offered free voice and video calls between users and became one of the most widely used VoIP platforms globally.
- 2010s: Integration with Unified Communications: VoIP became a crucial component of Unified Communications (UC) systems, integrating message, video, phone, and collaboration features into one platform. Within organizations, this integration improved communication and teamwork. This integration enhanced communication and cooperation within organizations.
- Present: Cloud-Based VoIP and Mobile Integration: Cloud-based VoIP services have become prevalent, allowing businesses to access advanced telephony features without significant infrastructure investments. VoIP calls may now be placed and received using smartphones thanks to standard mobile integration.
VoIP protocols and standards
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) relies on some protocols and standards to support communication over IP networks. The most prevalent protocols are as follows:
- Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): A signaling protocol called SIP is used to start, stop, and modify real-time sessions for messaging, video, and other communications apps and services.
- Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP): RTP is a protocol that transports audio and video over IP networks, ensuring real-time delivery and synchronization of multimedia.
- H.323: An older protocol suite for VoIP, H.323 encompasses various standards for multimedia communication, including voice and video, over IP networks.
- Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP): MGCP is a signaling and control protocol used to manage the communication between VoIP gateways and call control devices.
- H.248 (Megaco): This protocol controls the elements in a physically decomposed multimedia gateway, separating the call control and media gateway functions.
- Session Description Protocol (SDP): SDP defines multimedia communication sessions used for session announcements, invites, and other types of multimedia session initiation.
- RTP Control Protocol (RTCP): RTCP works alongside RTP to provide control and feedback on the quality of service in a VoIP session, including statistics and reports.
How Does VoIP Work?
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) converts analog audio signals into digital data packets sent across IP networks. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how VoIP works:
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion: The process begins when an analog voice signal (from a microphone or traditional phone) is converted into digital data. This conversion is typically done using a codec (coder-decoder).
- Packetization: The digital data is then segmented into small packets, each containing a portion of the voice data. These packets are labeled with headers containing information like source and destination addresses.
- Signaling: VoIP uses signaling protocols (e.g., SIP, H.323) to establish, modify, and terminate communication sessions. Signaling communicates information about call setup, call termination, and other control functions between devices.
- Transmission: The digital voice packets are transmitted over the Internet or an IP network. They travel through routers and switches, similar to other data packets.
- Routing: Routers direct the voice packets through the most efficient path to reach the destination. This can involve multiple hops across various network nodes.
- Internet Protocol (IP) Network: VoIP transmits voice data over existing IP networks, such as the Internet or private IP networks inside organizations.
- Reassembly: The digital packets are reassembled into a continuous digital data stream at the receiving end.
- Digital-to-Analog Conversion: The digital data is converted into analog signals using a codec at the receiving end.
- Playback: The analog signals are played through speakers or a handset, allowing the recipient to hear the transmitted voice.
VoIP configurations
1. Dedicated Routers
Dedicated routers are essential devices for utilizing Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services. These routers enable you to use your traditional phone to make VoIP calls. Connected to cable/DSL modems or any high-speed internet source, you can attach an ordinary telephone. Once configured and paired with an appropriate VoIP provider and service plan, these devices necessitate no special software or interaction with a computer. Pick up your phone, dial a number, and enjoy the call. Additionally, the portability of these routers allows users to bring their adapters while traveling, enabling them to make calls wherever broadband internet access is available.
2. Adapters (USB)
USB adapters provide another avenue for using a traditional phone for VoIP calls. Typically, these devices come in the form of USB adapters slightly larger than a typical thumb drive. Featuring a standard modular phone jack, they allow you to connect an ordinary phone line. Once connected, your phone functions as if it were linked to standard phone service. Behind the scenes, the included software sets up the VoIP call seamlessly.
3. Software-Controlled VoIP Applications: “Softphones”
Various software applications, commonly referred to as “softphones,” empower users to make VoIP calls directly from an ordinary computer equipped with a headset, microphone, and sound card. Often provided by Internet telephony service providers, these softphones are bundled with the requirement to use their specific service. This software-based approach is attractive to consumers as they may already possess the necessary components, making it a cost-effective option. Softphones and associated services allow users to communicate with others on the same service at no cost and connect with the rest of the world for a fee.
4. Dedicated VoIP Phones
Dedicated VoIP phones resemble traditional phones but connect to a computer network instead of a phone line. These phones may consist of a handset and a base station that connects to the internet or operate on a local wireless network. Similar to VoIP adapters, dedicated VoIP phones require a provider and service plan for seamless functionality.
5. Mobile VoIP Apps
Mobile VoIP applications have gained popularity, allowing users to make calls using their smartphones over the internet. These apps typically use Wi-Fi or mobile data connections to establish VoIP calls, offering flexibility and cost savings, especially for international calls.
6. Integrated VoIP Features in Business Phone Systems
Many modern business phone systems come equipped with integrated VoIP features. This integration enables businesses to combine traditional telephony with VoIP capabilities, providing enhanced communication options, cost savings, and scalability.
Types of VoIP Services
Various types of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services cater to different needs and preferences. Here are some common types:
- Residential VoIP Services: Designed for home users, these services provide cost-effective alternatives to traditional landline services. They often offer unlimited domestic calling and competitive international rates.
- Business VoIP Services: Tailored for businesses, these services provide advanced features like auto-attendants, call queuing, conferencing, and integration with business applications. They are scalable to accommodate the needs of small to large enterprises.
- Mobile VoIP Services: Mobile VoIP apps enable users to call using their smartphones over Wi-Fi or mobile data networks. Examples include apps like Skype, WhatsApp, and Viber.
- Free VoIP Services: Some providers offer free VoIP services for users making calls within their network or using their apps. While the initial service is free, additional features or calls to external numbers may incur charges.
- Paid VoIP Services: These services often provide enhanced call quality, additional features, and customer support. Users typically pay a monthly subscription fee or a pay-as-you-go model for the services used.
- Cloud-based VoIP Services: VoIP services are hosted in the cloud; thus, no on-premises gear is required. Businesses like it because of its scalability, flexibility, and management simplicity.
- On-Premises VoIP Systems: Some businesses prefer to host their VoIP systems on-site, giving them complete control over the infrastructure. This involves purchasing and maintaining the necessary hardware and software.
- VoIP Reseller Services: Companies or individuals can become VoIP resellers, offering VoIP services to their customers. They often purchase services from larger providers and sell them to end-users with additional value-added services.
- International VoIP Services: These services focus on providing cost-effective international calling rates. They are beneficial for individuals or businesses with significant global communication needs.
- Emergency VoIP Services: Some VoIP providers offer E911 (Enhanced 911) services, ensuring that emergency services can accurately locate and respond to calls made over the VoIP network.
- Wholesale VoIP Services: Designed for businesses or carriers that require large volumes of voice traffic, wholesale VoIP services provide cost-effective solutions for handling high call volumes.
VoIP in Business
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has become a staple in business communication due to its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and advanced features. Here’s how VoIP is used in the business context:
- Cost Savings: VoIP is frequently less expensive than traditional phone networks, especially for long-distance and international calls. Businesses may save money on both hardware and maintenance.
- Unified Communications: VoIP integrates with other communication tools, creating a unified platform. This includes features like video conferencing, instant messaging, and collaboration tools, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Scalability: The scalability of VoIP systems allows businesses to adjust phone lines to meet changing needs quickly.
- Remote Work: VoIP allows remote and mobile workers to communicate in real-time. Employees may access the company phone system from any location with an internet connection, fostering cooperation and flexibility.
- Advanced Features: Auto-attendants, voicemail-to-email, call forwarding, and call recording are just a few of the sophisticated capabilities of VoIP systems. These characteristics boost productivity and professionalism.
- International Presence: Businesses can establish virtual phone numbers in different countries, creating a global presence without physical offices. This can be beneficial for customer support or sales outreach.
- Integration with Business Applications: VoIP can integrate with customer relationship management (CRM) and other business applications. This integration streamlines workflows and provides a more comprehensive view of customer interactions.
- Conference Calling: VoIP facilitates high-quality conference calls and video conferencing. This is crucial for businesses with remote teams or meeting with clients and partners worldwide.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Management: Businesses can prioritize voice traffic over their network, ensuring high-quality calls by implementing QoS settings. This helps maintain a reliable and consistent communication experience.
- VoIP Analytics: Businesses can analyze call data to gain insights into communication patterns, call volume, and customer interactions. This information can inform decision-making and improve customer service.
- Security Measures: VoIP systems incorporate security measures such as encryption to protect sensitive business communications from eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
- Reliability and Redundancy: Many VoIP providers offer redundancy and failover options to ensure business continuity, even in network issues or hardware failures.
Advantages in VoIP
- VoIP often offers lower costs for domestic and international calls than traditional telephone services, especially for long-distance calls.
- VoIP offers unmatched flexibility by allowing people and companies to make and take calls from anywhere with an internet connection.
- VoIP systems can quickly scale up or down to accommodate changing business needs without significant infrastructure changes.
- VoIP systems improve communication capabilities with various services, including voicemail, call forwarding, video conferencing, and more.
- VoIP can seamlessly integrate with other business applications, improving overall efficiency and productivity.
- VoIP enables a global presence, allowing businesses to establish virtual offices with local phone numbers in different locations.
- VoIP integrates various communication channels, including voice, video, and messaging, into a unified platform for a streamlined user experience.
- Advanced VoIP systems provide built-in redundancy and failover options, ensuring service continuity even in network issues.
- VoIP systems are typically easier to maintain than traditional phone systems, and updates can often be performed remotely.
- VoIP generally has a lower environmental impact than traditional telephony, as it relies on the Internet and requires less physical infrastructure.
Future Trends in VoIP
- 5G Integration: The rollout and widespread adoption of 5G networks are expected to enhance VoIP services, providing faster and more reliable connectivity, reduced latency, and improved overall call quality.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI may play a more significant role in VoIP systems, providing intelligent call routing, voice recognition, and natural language processing to enhance user experiences.
- Enhanced Security Measures: VoIP systems will probably include increasingly sophisticated encryption protocols and security measures to guard against new threats as cybersecurity becomes increasingly important.
- Edge Computing for Reduced Latency: Edge computing can reduce the latency in VoIP services by processing data closer to the source, leading to improved call quality and responsiveness.
- Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS): Integrating VoIP into comprehensive, suitable communications platforms, including messaging, video conferencing, and collaboration tools, will likely become more prevalent.
- Blockchain for Security: Blockchain technology may enhance the security and privacy of VoIP communications by providing a decentralized and tamper-resistant record of call data.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: VoIP systems may increasingly interact with IoT devices, enabling a more connected and automated communication environment.
- Voice Biometrics: Using voice biometrics for authentication purposes in VoIP systems could become more widespread, offering an additional layer of security.
- Customization and Personalization: VoIP services could give customers greater personalization choices to adjust features to suit their requirements and tastes.
- Environmental Considerations: As environmental sustainability becomes a more significant concern, VoIP services may focus on energy efficiency and eco-friendly practices.
Case Studies
Skype:
Skype is one of the pioneers in the VoIP industry. Founded in 2003, Skype allowed users to make voice and video calls over the internet. Microsoft acquired Skype in 2011. It revolutionized long-distance communication and became a widely used platform for both personal and business purposes.
Vonage:
Vonage is a well-known provider of residential and business VoIP services. Founded in 2001, it played a crucial role in popularizing VoIP for consumers. Vonage’s services include unlimited calling plans and features like voicemail, call waiting, and caller ID.
Zoom:
While initially recognized for its video conferencing capabilities, Zoom also incorporates VoIP for audio communication. Its surge in popularity, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, showcased the effectiveness of VoIP in supporting remote work and virtual meetings.
RingCentral:
RingCentral is a cloud-based platform that provides communication and collaboration services and VoIP features. Many businesses use RingCentral for its unified communication features, such as voice, video, team messaging, and collaboration tools.
WhatsApp Calling:
WhatsApp, a popular messaging app owned by Facebook, introduced voice-calling features in 2015 and video calling later. It leverages VoIP technology to enable users to make calls over the internet, reducing the reliance on traditional cellular networks.
Cisco Webex Calling:
Cisco Webex is known for its collaboration solutions, including Webex Calling, a cloud-based VoIP service. It provides businesses with a scalable and feature-rich communication system, integrating voice, video, and messaging.
Ooma:
Ooma provides Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services for residential and business customers. Known for its straightforward pricing and user-friendly approach, Ooma provides features like virtual receptionists, call forwarding, and voicemail for its users.
8×8:
8×8 is a cloud communications platform providing VoIP services for businesses. It offers various communication tools, including voice, video, chat, and contact center solutions. 8×8 is known for its flexibility and scalability, making it suitable for multiple business sizes.
JioMeet:
JioMeet, launched by Reliance Jio in India, is a video conferencing platform incorporating VoIP for audio communication. It gained popularity, especially during the rise of remote work and virtual meetings.
Shoretel (Now Mitel):
Shoretel, now part of Mitel, provides unified communication solutions, including VoIP services. Mitel’s VoIP systems cater to businesses of different sizes, offering features like IP telephony, collaboration tools, and contact center solutions.
Conclusion
VoIP technology has revolutionized industries worldwide by simplifying global communication, reducing costs, enhancing online learning, and making telehealth services more secure. The case studies underscore VoIP’s adaptability in addressing specific challenges, fostering collaboration, and improving overall business operations. VoIP is positioned to play a significant part in influencing the direction of communication as technology develops further. It provides scalable and affordable solutions that enhance productivity and connection in a dynamic corporate environment.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP)” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,
What Is R Programming Language
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Applications of Machine Learning
Are you preparing for the entrance exam ?
Join our IT & Software test series to get more practice in your preparation
View More