
Definition of Splunk vs Elasticsearch
Splunk vs Elasticsearch are different from each other, both are the biggest enterprise solutions used for the analytics of logs. Elasticsearch is nothing but a database search engine, and Splunk is used for monitoring, visualizing, and analyzing the data. Elasticsearch will store the data and after storing analyze the data, whereas Splunk is used to analyze and monitor the machine data. The biggest disadvantage of Splunk is its paid tool.
Table of contents
Difference Between Splunk vs Elasticsearch
The main difference between Splunk and Elasticsearch is that Splunk is a paid tool, whereas Elasticsearch is an open source. We do not have to pay any cost while using Elasticsearch in our environment. Splunk and Elasticsearch are both used to analyze machine data. Multiple companies are using Elasticsearch in their environment, like Udemy and Uber. Splunk is also used in multiple companies like Blend and Yelp.
Basically, the Elasticsearch tool is integrated with Kibana and Logstash to work the same as Splunk. Apart from this, it will also be integrated with the other tools. Splunk is also integrated with multiple tools like Google Anthos and PagerDuty. Splunk is not an open-source tool, whereas Elasticsearch is open source tool.
What is Splunk?
Splunk is nothing but a tool or software platform that is used to analyze and monitor data. Splunk analyzes the real-time data generated by a machine. The data can come from web applications and websites, or it can also be created by the user. Splunk is not free to use, but it offers commercial solutions for free for 15 days as a free trial. Splunk is released in 2003. We can also analyze structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data using Splunk.
We mainly use Splunk for the analysis of big data. Splunk is similar to Logstash, Kibana, ELK, and Elasticsearch for visualization and storage. Splunk is also part of the product that was made by the company name laser-focused. Splunk provides software designed for clients to log a large amount of data. We can integrate Splunk with on-premises as well as cloud data stacks.
What is Elasticsearch?
Basically, Elasticsearch is an open-source tool, we can easily deploy and operate the same. We do not have to buy the license Elasticsearch before using it in our environment. We use Elasticsearch for analytics and to search our logs. It is a NoSQL database that stores unstructured data in a documented format. We can handle both structured and unstructured data with Elasticsearch.
Elasticsearch performs all three analyses, search operations, and visualizations of the data by integrating with Kibana and Logstash tools. The integration of Elasticsearch with Kibana and Logstash is known as the ELK. Elasticsearch is a very popular monitoring tool in day-to-day life.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Splunk vs Elasticsearch (Infographics)
Below are the top 10 differences between Splunk and Elasticsearch:
Key Differences Between Splunk vs Elasticsearch
Let us look at the key differences between Splunk and Elasticsearch:
- Elasticsearch was released in 2010, at a time when people were trying to compare the performance of Splunk with other tools. Splunk was released in 2003. It comes when we need to capture the machine data and logs.
- Elasticsearch does not contain any pre-loaded features and wizards, even it will not contain any interactive UI so that users can install the plugin. Splunk comes with pre-loaded features and wizards which are very easy to use.
- In Elasticsearch, we define the mapping type of each field to its specified value. Splunk will contain inbuilt and pre-defined features that enable the user to map data into entities and their respective values.
- We integrate the Elasticsearch tool with Kibana and Logstash. We can integrate Splunk with OverOps.
- Splunk improves its UI with controls and new dashboards. It contains the feature to export the dashboards in PDF format. Elasticsearch does not contain its UI, we need to install Kibana while performing the task.
Splunk Requirement
Splunk supports the Splunk enterprise on multiple computing environments. The Splunk data stream processor supports many hardware and software versions, and also it supports Splunk forwarders 7.0 and above.
Splunk supports the following browser version as follows. It will support multiple types of browsers.
- Chrome
- Safari
- Firefox
- Microsoft Edge
DSP generally works on a newer version of Linux. We are using Splunk on the following operating system are as follows.
- Amazon Linux
- Centos 7
- RedHat 7 and 8
- Ubuntu 16 and 18
While using Splunk cluster we require a minimum of three nodes cluster. Below are the hardware requirements of Splunk as follows.
- CPU cores – Minimum 8 physical and 16 vCPU. Recommended 16 physical and 32 vCPU.
- CPU architecture – x86 (64 Bit)
- Network speed – 10 Gb/s or higher
- Memory – 64 GB and 128 GB
Elasticsearch Requirement
Elasticsearch contains specific hardware requirements for storage and memory. The host machine will support the x84 – 64-bit instruction set. While using Elasticsearch we have required minimum memory is 8 GB. For small deployment it will require 32 GB, for medium deployment, it will require 32 GB and for large deployment, it will require 128 GB.
The Elasticsearch management services are provided to the directors and coordinators which require fast SSD storage to work correctly. Allocators are supporting our Elasticsearch clusters and the instances of Kibana. While using Elasticsearch we have recommended that use 128 or 256 GB of memory.
Comparison Table of Splunk vs Elasticsearch
The table below summarizes the comparisons between Splunk vs Elasticsearch:
| Splunk | Elasticsearch |
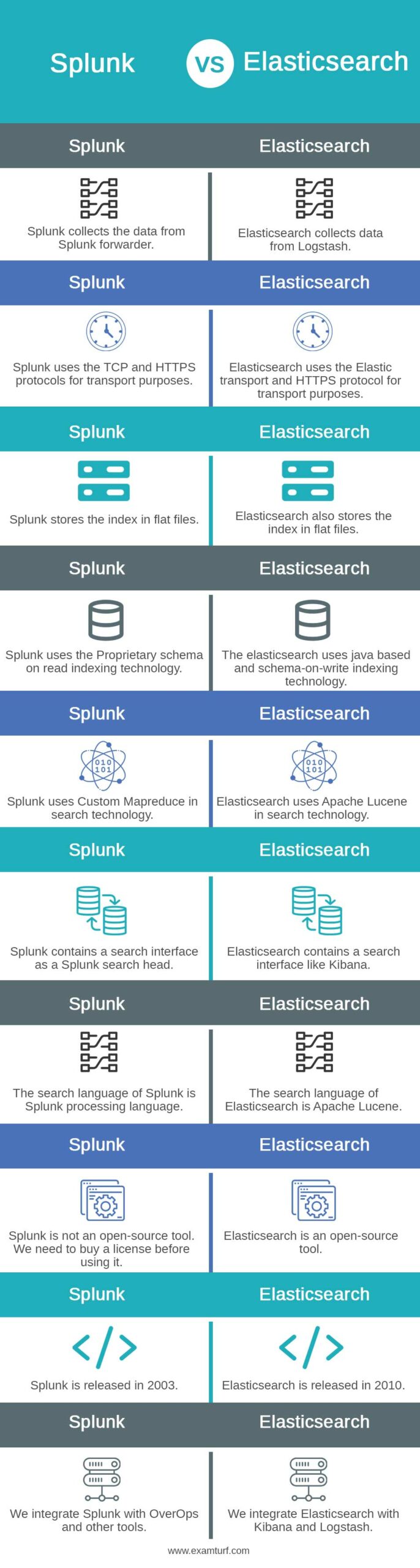
| Splunk collects the data from Splunk forwarder. | Elasticsearch collects data from Logstash. |
| Splunk uses the TCP and HTTPS protocols for transport purposes. | Elasticsearch uses the Elastic transport and HTTPS protocol for transport purposes. |
| Splunk stores the index in flat files. | Elasticsearch also stores the index in flat files. |
| Splunk uses the Proprietary schema on read indexing technology. | The elasticsearch uses java based and schema-on-write indexing technology. |
| Splunk uses Custom Mapreduce in search technology. | Elasticsearch uses Apache Lucene in search technology. |
| Splunk contains a search interface as a Splunk search head. | Elasticsearch contains a search interface like Kibana. |
| The search language of Splunk is Splunk processing language. | The search language of Elasticsearch is Apache Lucene. |
| Splunk is not an open-source tool. We need to buy a license before using it. | Elasticsearch is an open-source tool. |
| Splunk is released in 2003. | Elasticsearch is released in 2010. |
| We integrate Splunk with OverOps and other tools. | We integrate Elasticsearch with Kibana and Logstash. |
Purpose of Splunk
Splunk is used to analyze the aggregated logs from the big clusters. We are using Splunk with big data for analyzing the logs. While using Splunk, we can analyze the log at high speed, and the log is real-time. Splunk gives alerts and reports of the desired search. Splunk is used to troubleshoot and resolve the issue also, it will give quick results.
While using Splunk, we can enhance the real-time visibility of multiple formats. We have no need for other dependent services while using Splunk in our environment. We can set up Splunk easily; also it will contain low maintenance. By using Splunk, we can directly upload the data from locally to Splunk.
Purpose of Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is open-source, we are using this software for analyzing and managing the logs. Elasticsearch is a clear application, it will use the stack for checking errors.
Elasticsearch provides good stats of visualization. Elasticsearch collects authentication information from the providers, which is a good feature of this tool. Elasticsearch software contains scalability. Elasticsearch is easy and simple. Also it is more user-friendly. By using Elasticsearch, log reports is very clean, and reports come within minutes. Elasticsearch is working with a discoverer.
Conclusion
Elasticsearch will store the data and after storing, analyze the data, whereas Splunk is used to analyze and monitor the machine data. The biggest disadvantage of Splunk is its paid tool. The main difference between Splunk and Elasticsearch is that Splunk is a paid tool whereas Elasticsearch is an open source, we have no need to pay any cost while using Elasticsearch in our environment.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Splunk vs Elasticsearch. Here we discuss Splunk vs Elasticsearch key differences with infographics and a comparison table in detail. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –
Are you preparing for the entrance exam ?
Join our Data Science test series to get more practice in your preparation
View More