Definition of Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics
Predictive vs prescriptive analytics is not straightforward, it will take descriptive data and transform same into information. Predictive and prescriptive analytics is informing our business strategies based on the data. While prescriptive analytics assists you in formulating precise recommendations, predictive analytics projects likely future results. The use of both analytics can transform descriptive measurements into conclusions and recommendations. However, we shouldn’t rely on just one sort of analytics.
Table of contents
- Definition of Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics
Difference Between Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics
While combining predictive and prescriptive analytics, we can change your business plan and achieve the greatest results. To stay competitive in the increasingly cutthroat market, predictive analytics alone is insufficient. For practically any application or business process, prescriptive analytics offers recommendations for the best next steps to take in order to expedite or drive desired outcomes.
Both are crucial tools for business, and each has a place in it. Predictive analytics, however, is beneath prescriptive analytics in the Gartner hierarchy of analytics, which was mentioned above. This is due to the fact that predictive analytics predicts that does not provide direction for necessary decisions. Prescriptive analytics, on the other hand, not only predicts what will happen but also identifies the optimal course of action for the organization.
What is Predictive Analytics?
An advanced analytics subcategory called “predictive analytics” aids businesses in understanding probable outcomes or the effects of an action. Predictive analytics employs raw, current data to look into the future by using mining data, historical data, and statistics. Predictive analytics used to be exclusive to enterprise-level companies, who could pay to analyze and understand reams of data from many sources. However, thanks to the expansion of CRM analytics and SaaS suppliers, even small businesses now have access to useful data analytics.
Predictive analytics may tempt one to view them as a method of telling. What it does provide is a way to employ modeling and statistical methods to create well-considered forecasts and outcomes for the business. There are three pillars of predictive analytics. To find dangers and opportunities, predictive analytics uses historical data.
What is Prescriptive Analytics?
Although it takes a more technological approach, prescriptive analytics also considers potential future events. The probable future event is examined in greater detail using sophisticated mathematical algorithms and machine learning. A business can view a variety of options and potential consequences with the use of prescriptive analytics. Prescriptive analytics can adjust its forecasts and recommendations in response to new data.
Emerging as a more sophisticated application of predictive analytics is prescriptive analytics. Prescriptive analytics does more than just anticipate possible outcomes using a predictive model. In fact, it makes a number of recommendations along with possible results for each action. A business can finally develop a more unified business plan with the use of a prescriptive model.
Head to Head Comparison Between Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics (Infographics)
Below are the top 10 differences between Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics:
Key Differences Between Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics
Let us look at the key differences between Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics:
- Using historical data, predictive analytics makes predictions about likely future consequences. Producing specific recommendations for prescriptive analytics makes extensive use of data.
- Structured historical data is frequently used in predictive analytics (e.g. transactional data). Hybrid data, which combines unstructured input and previously specified structured data, is frequently used in prescriptive analytics (e.g. pictures).
- According to statistics, predictive analytics entails estimating the value of an unknown variable based on variables. The goal of prescriptive analytics is to improve one or more performance indicators by discovering the best variable.
- Based on the same data predictive analytics model produces the same predictions. Prescriptive analytics models must be updated frequently with fresh data to maintain their relevance.
- We can use prescriptive analytics to further analyze the basis of raw data that predictive analytics has provided. In other words, while prescriptive does the labor-intensive analysis, predictive delivers huge data.
Predictive Analytics Requirement
At the time working with predictive analytics data, we need to consider whether our data is capable of providing an answer to our question. There are multiple factors that determine the appropriateness of the data. While deciding on the data sources, the cleanliness of the data sources is assessed and it is more useful.
After cleaning the data we need to define machine learning and automation in the data. In the machine, we are using multiple algorithms on data to sort and clean the data for user use. After applying algorithms and machine learning algorithms, not in the final step, we are checking whether our analytics is meeting the business objectives or not.
Prescriptive Analytics Requirement
A typical business has an online footprint, therefore the owner or operator must gather, ingest, analyze, and display the data to generate competitive information. As they are often highly busy managing their day-to-day operations, business owners and operators lack the free time to seek data technology, and more particularly, improved business analytics, for more financial gain.
They require solid profit margins, nevertheless, in order to survive in the long run. For majority of the business owners who operate in this manner, all data technology responsibilities must be handled and managed by a data center, an advanced data analytics team, or an external data service provider.
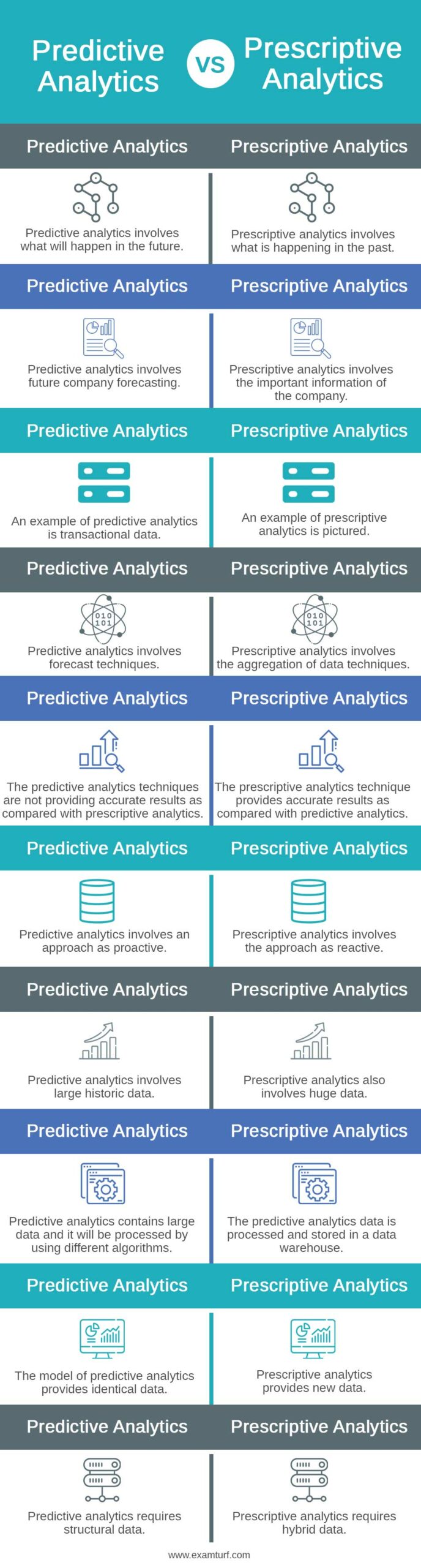
Comparison Table of Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics
The table below summarizes the comparisons between Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics:
| Predictive Analytics | Prescriptive Analytics |
| Predictive analytics involves what will happen in the future. | Prescriptive analytics involves what is happening in the past. |
| Predictive analytics involves future company forecasting. | Prescriptive analytics involves the important information of the company. |
| An example of predictive analytics is transactional data. | An example of prescriptive analytics is pictured. |
| Predictive analytics involves forecast techniques. | Prescriptive analytics involves the aggregation of data techniques. |
| The predictive analytics techniques are not providing accurate results as compared with prescriptive analytics. | The prescriptive analytics technique provides accurate results as compared with predictive analytics. |
| Predictive analytics involves an approach as proactive. | Prescriptive analytics involves the approach as reactive. |
| Predictive analytics involves large historic data. | Prescriptive analytics also involves huge data. |
| Predictive analytics contains large data and it will be processed by using different algorithms. | The predictive analytics data is processed and stored in a data warehouse. |
| The model of predictive analytics provides identical data. | Prescriptive analytics provides new data. |
| Predictive analytics requires structural data. | Prescriptive analytics requires hybrid data. |
Purpose of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses statistics and modeling to find problems before they even occur. Only prospective future occurrences can be predicted using predictive analytics; actual future events cannot be predicted. The increased connection of newer aircraft generations has made it easier than ever to gather vast amounts of historical data. With the right methods, data is assessed to determine likely key risks beforehand.
Additionally, more timely maintenance results from precisely forecasting impending defects or breakdowns. Important inspections and fixes can be implemented before a problem becomes dangerous, which results in cheaper maintenance costs, improved component reliability, less need for inventory, and quicker maintenance turnaround times.
Purpose of Prescriptive Analytics
By providing clear and practical next steps for resolving the problems raised by the predicted data analysis, prescriptive analytics advances predictive analytics. Prescriptive analytics uses multiple layers of machine learning to recommend options for maximizing future possibilities or minimizing future hazards.
Prescriptive analytics processes hybrid data as well as business rules, to produce such robust information. The analytics systems are always fueled by AI, which means they are constantly ingesting fresh data to provide more precise predictions and better-defined decision possibilities. To obtain the best data possible, many techniques can be researched, merged, and improved upon using machine learning neural networks. Prescriptive analytics is therefore more effective than the human intellect at sorting, analyzing, learning from, and building upon data.
Conclusion
Predictive and prescriptive analytics informs our business strategies based on the data. While prescriptive analytics assists you in formulating precise recommendations, predictive analytics projects likely future results. Structured historical data is frequently used in predictive analytics (e.g. transactional data). Hybrid data, which combines unstructured input and previously specified structured data, is frequently used in prescriptive analytics (e.g. pictures).
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics. Here we discuss Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics key differences with infographics and a comparison table in detail. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –
Are you preparing for the entrance exam ?
Join our Data Science test series to get more practice in your preparation
View More